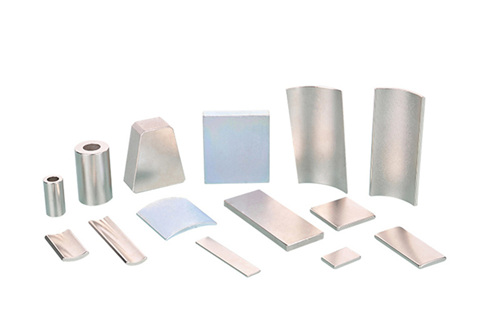
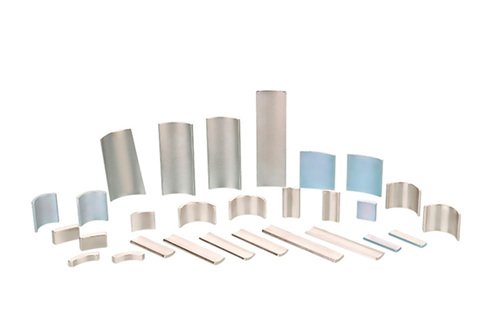
Introduction to Laminated Magnets
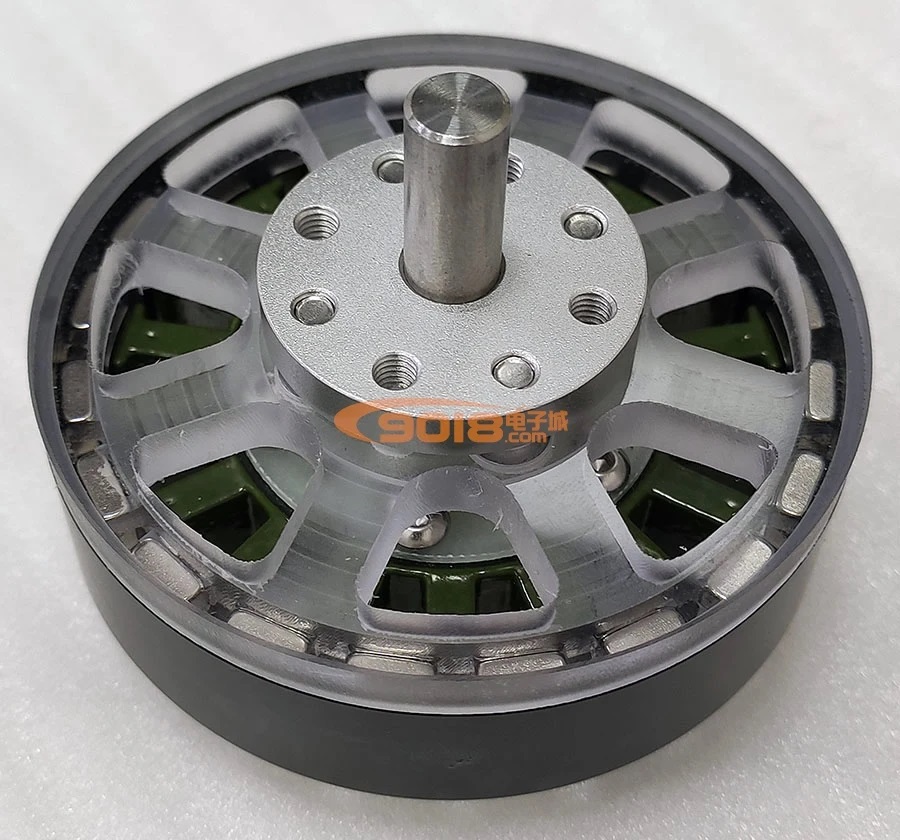
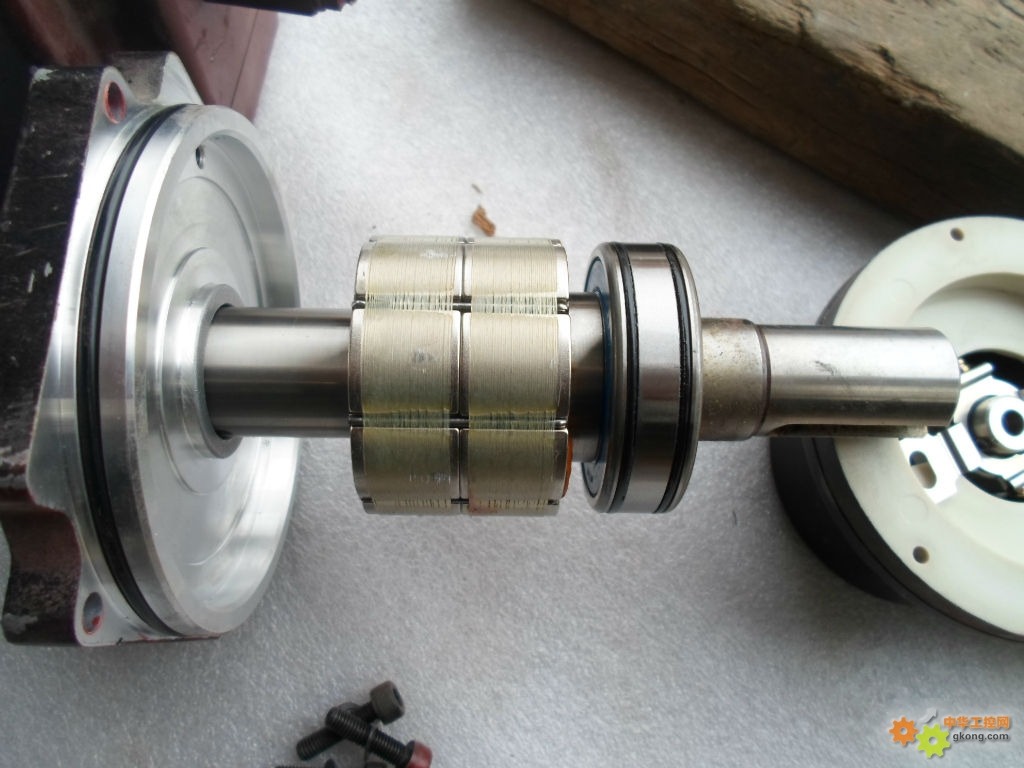
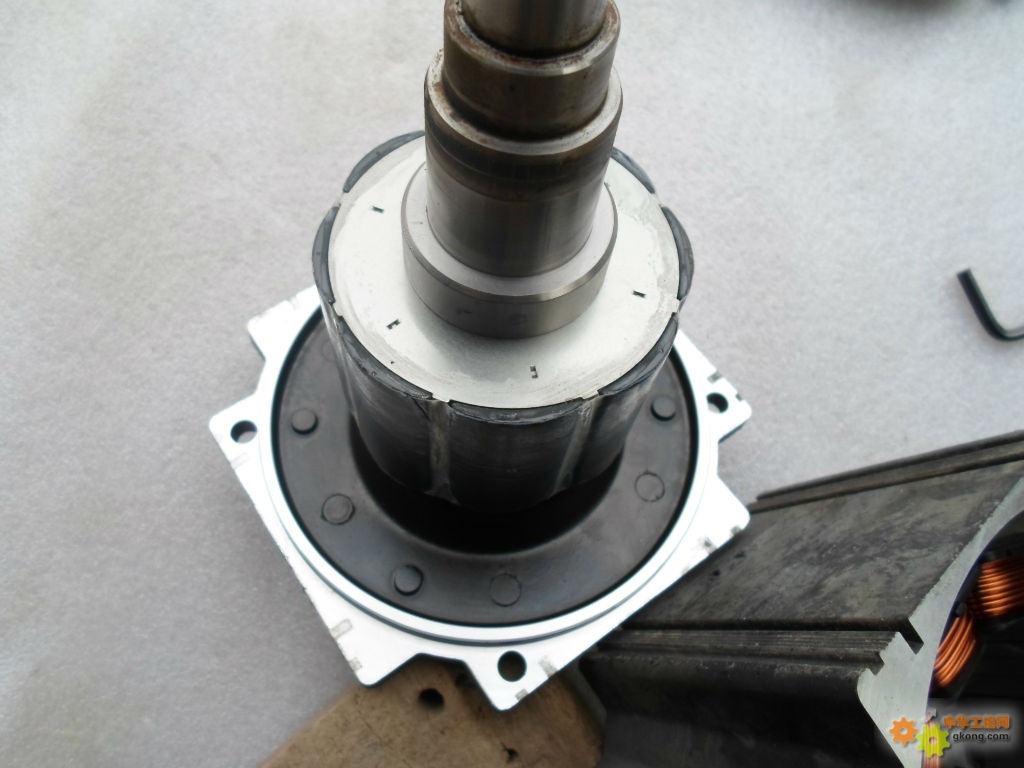
The laminated magnet is a type of magnet that consists of multiple thin layers (laminations) of magnetic material, which are stacked together with insulating layers in between. This design primarily aims to reduce eddy current losses, making laminated magnets especially useful in applications where the magnetic field changes rapidly, such as in alternating current (AC) devices.
Laminated magnets are specialized permanent magnets designed to mitigate eddy current losses, particularly beneficial in applications involving alternating current (AC) or rapidly changing magnetic fields. These magnets are constructed from multiple thin layers of magnetic material, each separated by an insulating layer, which helps to confine and reduce the eddy currents that can lead to energy loss and heat generation.
Laminated Rare Earth Magnets Key Features and Benefits:
Reduction of Eddy Current Losses:
Eddy currents are loops of electric current induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field. These currents generate heat and result in energy loss. Laminating the magnet restricts these currents to smaller, less significant loops, thereby minimizing energy losses and heat generation.
Improved Efficiency:
Reduced eddy current losses lead to higher efficiency in devices using laminated magnets. This is particularly beneficial in electric motors, transformers, and other electromagnetic devices where efficiency directly impacts performance and energy consumption.
Enhanced Performance in AC Applications:
Laminated neodymium magnets are particularly advantageous in applications where the magnetic field changes direction or magnitude frequently, such as in AC motors and generators. The laminations help maintain the performance of the magnet by reducing energy dissipated as heat.
Construction:
Material: Typically made from ferromagnetic materials like silicon steel or other high-permeability materials.
Structure: The magnet is composed of multiple thin layers of magnetic material, separated by an insulating adhesive or coating. These layers are stacked and bonded together to form the overall magnetic structure.
Reduced Heat Generation:
Lower eddy current losses mean less heat is generated, which helps maintain the integrity and performance of the magnet over time.
Energy Savings:
Enhanced efficiency translates to energy savings in applications where laminated magnet is used.
Extended Lifespan:
Reduced heat and energy losses contribute to a longer lifespan for devices using laminated magnets.